Cultivation of virus - microbiology notes
CULTIVATION OF VIRUS
- Virus are smallest obligate intracellular infective agent containing only one gene type of nuclei acid ( DNA/RNA) as their genome.
- Virus multiply only in living cells
- They cannot be grown on inanimate culture medium.
METHOD OF VIRUS CULTIVATION:
1)Animal inoculation
2) Embryonated egg inoculation
3) Tissue culture
1) ANIMAL INOCULATION:
Three main reason why animal inoculation is used for
- Primary isolation of certain viruses
- To study pathogenesis of viral diseases
- To study viral oncogenesis
- Isolation of arbovirus,coxsackie virus is done on INFANT MICE.
- Route of inoculation :intracerebral,subcutaneous,intranasal.
- After inoculation: animals are observed for sign of disease or death.
- Later on they are sacrificed and tissues are tested for the presence of virus.
- Other animal such as guinea pig,rabbit and ferrets are also used in some situation.
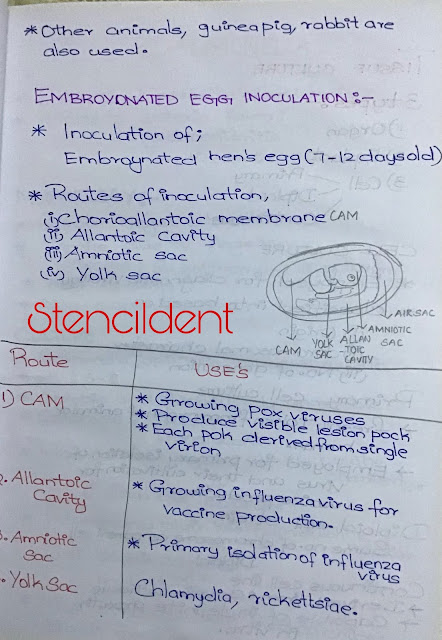
2 EMBRYONATED EGG INOCULATION
- Inoculation of embryonated hens egg ( 7-12 days old) are inoculated by one of the several routes.
Routes of inoculation :
1)chorioallantoic membrane:
- Chorioallantoic membrane is inoculated mainly growing poxviruses
- It produces visible lesions known as pocks
- Each pock is derived from a single verion.
2) ALLANTOIC CAVITY
- Allantoic inoculation is used for growing influenza virus for vaccine production.
3) AMNIOTIC SAC :
- Inoculation into the amniotic sac is mainly used for the primary isolation of the influenza virus.
4)YOLK SAC ;
TISSUE CULTURE;
3 TYPES:
1)ORGAN
2)EXPLANT
3) CELL :
Employed for diagnostic virology
classified into based on :
- origin
- chromosomal character
- number of generation
Freshly taken from organ of animal or human
employed for primary isolation of virus and their cultivation for vaccine production
DIPLOID CELL STRAIN:
Same number of chromosome as parent cell
CONTINUOUS CELL LINE:
Derived from a cancerous tissue
Its capable of indefinite growth in vitro.
A brief introduction on general properties of virus have been posted already do click on the LINK to understand much better about virus and do let me know in the comment section if you would like me to post about corona and it recent researches.
THANK YOU





Comments
Post a Comment