how do forensic odontologist use dental record to identify people?
FORENSIC ODONTOLOGY -PART 1
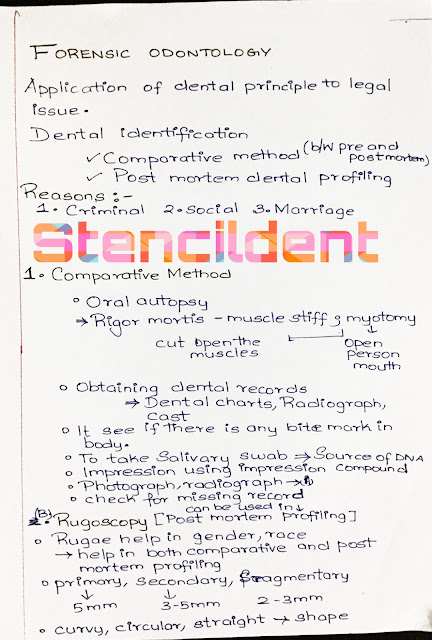
Forensic odontology : Application of dental principle to legal issue
Dental identification:
- COMPARATIVE METHOD
- POST MORTEM DENTAL PROFILING
COMMON REASONS FOR IDENTIFICATION OF FOUND HUMAN REMAIN?
- CRIMINAL: Investigation to a criminal death cannot begin until the victim has been positively identified
- SOCIAL: its society duty to preserve human rights
- Marriage: Individuals from many religious background cannot remarry unless their partners are confirmed deceased
- Closure: the identification of individual missing for prolonged period can bring sorrowful relief to family members
1) COMPARATIVE METHOD:
A)ORAL AUTOPSY
Rigor mortis -muscle stiffness ,myotomy to cut open the muscles
Obtaining dental records:
- Dental charts,radiograph,cast
- To see if there is any bite mark in the body
- To take salivary swab - source of DNA
- Photograph,radiograph
- Check for missing records
B) RUGOSCOPY ( POST MORTEM PROFILING)
- Rugae help in gender ,race ,it also helps in both comparative and post mortem profiling
- classification of rugae :
- a) based on size: primary ( >5mm),secondary(3-5mm),fragmentary(2<3mm)
- b)based on shape : straight,curvy,circular
- they use clear tracing sheet to draw rugae pattern
C) DNA PROFILING:
- Source : teeth (pulp),saliva,blood
- Types of DNA : Nuclear DNA,Mitochondrial DNA ( Maternal DNA)
- Extraction of DNA: Cryogenic grinding,scraping out pulp
- Analysis of dna :restriction fragment length polymorphism,polymerase chain reaction,microarrays.
- Compared to ante mortem ; hair from comb,biopsy specimen,toothbrush,parents or sibling DNA.
- Combined dna index system ( CoDIS)
D) HUNTER SCHREGER BAND PATTERN:
- Using software corel photo paint - contrast enhancement
- Antemortem record is required
E) EXAMINATION OF TOOTH PRINT ( AMELOGLYPHICS)
- Pattern of enamel
- area of tooth
- orthophosphoric acid is etched with acetone to acetate sheet
- limitation: tooth fractured,abrasion,decay - enamel rod orientation would change
POST MORTEM DENTAL PROFILING:
1) IDENTIFICATION OF GENDER OF PERSON:
A) MORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS
B)MOLECULAR ANALYSIS
C) MISCELLANEOUS
A) HARD TISSUE EXAMINATION : 1) ODONTOMETRIC 2) ORTHOMETRIC
SOFT TISSUE EXAMINATION: 1) RUGOSCOPY 2) LIP PRINT ( CHEILOSCOPY)
DENTAL INDEX:
MEAN CANINE INDEX =MESIODISTAL WIDTH OF MANDIBULAR CANINE/MANDIBULAR INTERCANINE WIDTH
Standard mean canine index - 0.274 ( if less than MCI ,then female)
ORTHOMETRIC:
MALE FEMALE
CRANIAL MASS Blocky massive rounder taper
temporal ridge more prominent less prominent
zygomatic bone more prominent less
mandible squared rounded
forehead rounded ,sloping terminate at brow
gonion flared sharply,angled less flared
teeth larger smaller
- The tabular column might get exchanged when viewed in phone ,kindly use laptop/ipad/ computer or refer the images for better clarity .
SOFT TISSUE EXAMINATION;
LIP PRINT ANALYSIS:
- Useful in comparative and post mortem profiling
- recorded by dividing the lip into quadrant
- limitation: mouth opened or closed pathology in lip,thick lipstick
- lip pattern region of occurrence 1st quadrant (R-UL)
- TYPE 1,2 FEMALE
- TYPE 2 2ND QUADRANT ( L-UL) MALE
- TYPE 3 NEVER OCCUR IN LOWER LIP MALE
(R-UL) - RIGHT UPPER LIP,(L-UL)- LEFT LOWER LIP
B) MOLECULAR ANALYSIS :
- BARR BODIES: deeply stained chromatin material female chromosome
- F bodies
- SRY gene - located on short ( p) arm of Y chromosome at the position 11.3
- AMEL GENE: Amelogenin is secreted by ameloblast ,AMEL Y GENE in 112th base pair
- female- 2 identical,male - 2 non - identical
C) MISCELLANEOUS METHOD;
- Dental prosthesis labelling
- Determination of race :
- Metric- tooth size ,shape
- Non-metric- shovelling,carabelli trait ,mandibular molar groove
AIM OF THIS POST :
Today we have learnt on what forensic odontology is? comparative method - rugoscopy,DNA profiling,hunter schreger band pattern,examination of tooth print then we moved on to post mortem dental profiling under which we learnt about how the gender of the person is been identified :morphological,molecular and miscellaneous analysis .hope this post would have been informative the next post is about how bitemarks on the victim helps in identification of the criminal .do let me know in the comment section below if this post helped you .
Contact details :
Email: stencildent@gmail.com
Instagram handle: stencildent
THANK YOU






Thank you so much doctor it means a lot to me 🙏🏻
ReplyDelete