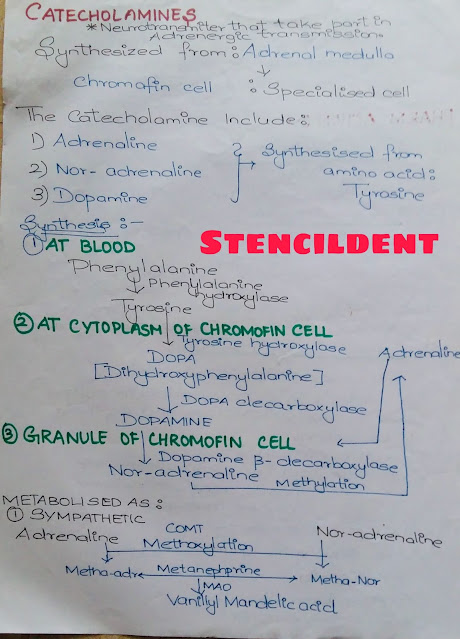
LOCAL ANAESTHETICS- PHARMACOLOGY NOTES

LOCAL ANAESTHETICS Drugs that block peripheral nervous tissue when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentration,without loss of consciousness CLASSIFICATION: A) INJECTABLE : SHORT ACTING : Procaine Chloroprocaine INTERMEDIATE ACTING Lignocaine Prilocaine LONG ACTING Bupivacaine Ropivacaine tetracaine B) SURFACE ANAESTHETIC: Lignocaine Cocaine Tetracaine MECHANISM OF ACTION : Primary mechanism of action: blockade of voltage gated sodium channel local anaesthesia diffuse through cell membrane to bind the voltage sensitive sodium channel to prevent generation of action potential and conduction DIFFERENTIAL BLOCKADE: 1)Autonomic (1st blocked )followed by sensory fibres,pain temperature ,touch ,pressure,vibration Non myelinated fibres are blocked readily than myelinated FEATURES OF LOCAL ANAESTHETICS: 1) It should have quick onset of action 2)It should not be irritating to skin and mucous...