CHERUBISM /FAMILIAL FIBROUS DYSPLASIA OF JAWS -Definition,Pathogenesis,Clinical features,Radiographic features,Histopathology and Treatment
CHERUBISM
SYNONYMS:
1)FAMILIAL FIBROUS DYSPLASIA OF JAWS
2)DISSEMINATED JUVENILE FIBROUS DYSPLASIA
INTRODUCTION:
- JONES in 1933 coined the term cherubism
- They resemble cherubs ( chubby cheeked little angel in renaissance painting)
- Autosomal dominant fibro-osseous lesion of jaws
DEFINITION:
- Rare inherited autosomal dominant disease that causes bilateral enlargement of jaws giving the child a cherubic facial appearance
- Regress with age ,composed of giant cell granuloma like tissue and does not form bone matrix
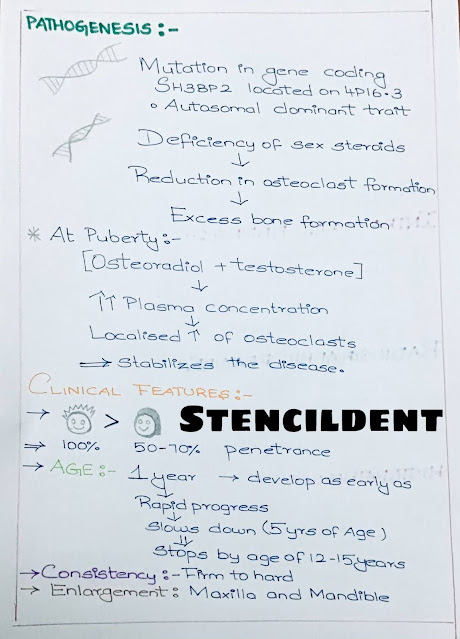
PATHOGENESIS:
- Mutation in gene coding SH3BP2 located on 4P16.3
- Autosomal dominant trait
- Deficiency of sex steroids leads to reduction in osteoclast formation which leads to excess bone formation
At puberty,
- Osteoradiol+testosterone will cause increase in plasma concentration which results in localised increase in osteoclast
Thereby,stabilizes the disease
CLINICAL FEATURES:
- Male's are more commonly affected than female ,100%penetrance in males,50-70% in females
- Age: Develop as early as 1 year ,rapidly progress ,slows down by the age of 5 years and stops by age of 12-15 years
- CONSISTENCY: firm to hard
- ENLARGEMENT: Maxilla and mandible
- SYMMETRY:Symmetrical,bilateral expansion
- LYMPH NODE:Cervical lymphadenopathy
- EYE: Upward gaze,EYE TO HEAVEN APPEARANCE:a rim of sclera below iris ,impaired vision
- RESPIRATORY :Obstruction
INTRA ORAL FINDING :
- Inverted V shaped palatal arches
- Premature loss of deciduous
- Displacement of teeth
- Missing teeth
- Delayed eruption
RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES:
- Bilateral multilocular expansile radiolucencies
FLOATING TOOTH SYNDROME :
- Teeth floating in cystic space appearance
- Displacement of inferior alveolar canal
HISTOPATHOLOGY :
- Eosinophilic cuffing around blood vessel
- Multiple multinucleated giant cells together with ovoid to spindle shaped cells with a fine fibrillar collagenous stroma
- Resolving lesions show fibrous connective tissue
- New bone formation (repair)
TREATMENT:
- No treatment until puberty
- Orthodontic treatment for malocclusion
After puberty,
- Aesthetic concerns - osteotomy
- Radiation -contra-indicated( increase risk of osteoradionecrosis ,osteosarcoma )
AIM OF THIS POST :
Today we started with a small introduction about cherubism its synonyms,then we moved into pathogenesis and we could clearly make it out its due to gene mutation and has a autosomal dominant trait ,clinical features ,intra oral finding ,radiographic and histopathologic features and finally concluded with treatment .Hope you found this post informative ,if it helped you learn then do let me know in the comment section below as this would motivate me to post more such content . Do stay connected through instagram as well to receive instant updates
CONTACT DETAILS :
EMAIL;stencildent@gmail.com
INSTAGRAM; stencildent
THANK YOU






Comments
Post a Comment